
![[sort:pic]](/template/default/images/banner/3-3.jpg)

Lean management provides customers with high-quality services and a visible panoramic view of the prosperous era.
Share
U.S.–China Tariff Truce Extended for Another 90 Days: Full Breakdown of Policy Details, Market Reactions, and Potential Impacts
Summary:
On August 12, 2025, President Trump signed an executive order extending the suspension of additional tariffs on Chinese goods—originally set to expire that day—until November 10, 2025 (12:01 a.m. EST).

The tariff delay was an expected outcome of U.S.–China trade talks held in Stockholm in late July.
Timeline:
• In April, the U.S. raised tariffs on Chinese goods to 145%. China retaliated with tariffs of 125% on U.S. products.
• In May, negotiations led to a temporary reduction: the U.S. lowered tariffs to 30%, China to 10%. Both sides also agreed to suspend part of the tariffs for 90 days.
• That suspension was first extended to August 12 and now further extended to November 10.
Reasons for Extension:
• Productive progress during the Stockholm trade talks
• China’s active steps to improve reciprocity and address U.S. economic and security concerns
• Consideration of the upcoming U.S. holiday shopping season, which requires a consumer confidence boost
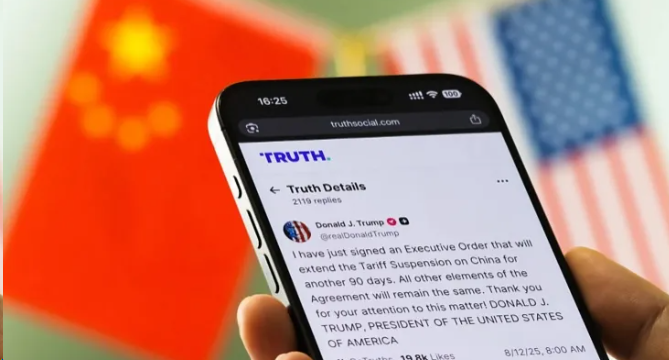
Markets responded quickly to the announcement.
1. Financial and Energy Markets
International oil prices weakened as the tariff extension eased concerns over a global economic slowdown, though geopolitical uncertainty added volatility.
Trump and Russian President Vladimir Putin plan to meet in Alaska to discuss the Ukraine conflict. If a ceasefire is reached, oil prices could face further downward pressure.
2. Technology and Manufacturing
Uncertainty in tariff policy has pushed major tech companies to adopt proactive measures:
• NVIDIA, AMD: Agreed to remit 15% of revenue from sales to China to the U.S. government in exchange for permission to continue selling high-end chips in China.
• Apple: Pledged to invest $600 billion in the U.S. over the next four years and has already secured partial tariff exemptions.
Analysts note that this “investment-for-relief” model could spark a “domino effect” across industries, especially for tech firms heavily reliant on global supply chains.
3. Food and Consumer Goods
While overall food prices held steady month-over-month in July, tariff-sensitive goods saw sharp year-over-year increases:
• Eggs: +16.4%
• Coffee: +14.5%
• Beef: +11.3%
• Candy & chewing gum: +7.5%
Weather disasters, global supply chain disruptions, disease outbreaks, and rising import tariffs have compounded pressure on small businesses in the food sector. For instance, U.S. café owners have been forced to raise prices frequently, and some even added extra surcharges to cope with soaring costs.
Experts predict that the full ripple effects of the new tariffs will likely be felt during the holiday season—especially after August 29, when the de minimis exemption for goods under $800 will be removed, directly impacting retail goods.

Walmart, for example, has introduced a year-round 10% discount on nearly all groceries (including milk, meat, and frozen foods) for its 1.6 million U.S. employees, aiming to offset cost-of-living pressures while also helping with worker recruitment and retention.
Walmart executives admitted that the current level of tariff hikes has exceeded what retailers can absorb and that further price increases are expected.

We will continue to monitor developments in tariff policies.